Heat engines
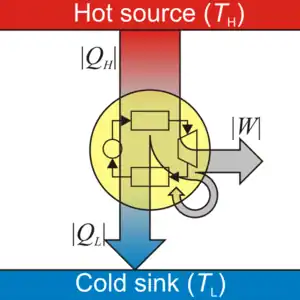
Heat engines are machines which accept energy from a hot heat source, convert a fraction of it to work, and reject the remainder to a cold heat sink. The maximum possible fraction converted to work is . (T_hot - T_cold) / T_hot.
Heat engines which use renewable energy derive it from the sun or from hot geothermal sources, which derive from natural nuclear fission inside the earth. Or the hot source may derive its energy from burning biomass.
These are commonly called Sterling Engines or Carnot cycle engines.
See also
External links
| Authors | Anonymous1 |
|---|---|
| License | CC-BY-SA-3.0 |
| Cite as | Anonymous1 (2006–2025). "Heat engines". Appropedia. Retrieved November 28, 2025. |