Fuel-powered turbine
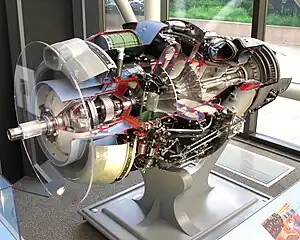
A fuel-powered turbine is a turbine that is powered by a fuel (ie a liquid or a gas).[1] Unlike ie steam turbines, the fuel burned is immediatelly used to turn the turbine blades. As such, the step of converting fuel to steam is skipped and fuel-powered turbines are hence more efficient then steam turbines. This article specifically focuses on turbines of a small size intented for the purpose of local electricity supply.
Types
Both gas and liquid-fueled microturbines should be distinguished, as they vary slightly in regards to the design.
DIY gas and liquid-fueled microturbines
The simplest form of self-constructed gas turbine employs an automotive turbocharger as the core component. A combustion chamber is fabricated and plumbed between the compressor and turbine sections.[2][3] The Schreckling design[4]constructs the entire engine from raw materials, including the fabrication of a centrifugal compressor wheel from plywood, epoxy and wrapped carbon fibre strands.[4]
Commercial microturbines
Several companies have started to produce microturbines, mostly for the purpose of energy production, as well as for use as a "range extender" in electric vehicles.[5]
Notable companies are:
- Bowman Power produces the TurbogenTM microturbines
- Capstone
- Elliot Energy Systems
- Ingersoll-Rand (IR)
- Turbec AB
- Micro Turbine Technology BV
- Bladonjets
Some other companies as Garrett and Deutz also produce microturbines[6][7]
See also
- Wind turbine: another form of turbine
- Holzwarth gas turbine
- Pulse jet engine
References
- http://www.bioturbine.org/Workshop/BIOTURBINE-Workshop-DraftAgenda-040922.pdf
- http://www.bioliquids-chp.eu/index.php?id=37&rid=12&r=algemeen
- ↑ Biofuel turbine engine term
- ↑ Homemade turbine projects
- ↑ "UK TV series, "Scrapheap Challenge", "Jet Racer" episode". 2003.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Schreckling, Kurt (1994). Gas Turbines for Model Aircraft. ISBN 0-9510589-1-6.
- ↑ [ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Range_extender#Range_anxiety_elimination Range extenders]
- ↑ Garrett GTP 30-67 used by University of Florence
- ↑ Deutz T216 turbine
External links
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gas_turbine#Microturbines
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gas_turbine#Amateur gas turbines
- http://www.lambert-modellturbinen.de/html/english.html
- http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:GasTurbine.jpg
- http://web.archive.org/web/20160322021446/http://www.wbdg.org:80/images/media_img.php?m=microturbines_4lg.jpg&w=488&h=330
- http://www.wbdg.org/resources/microturbines.php
| Authors | KVDP |
|---|---|
| License | CC-BY-SA-3.0 |
| Cite as | KVDP (2012–2025). "Fuel-powered turbine". Appropedia. Retrieved November 28, 2025. |